Wave Propagation
[pdf manuscript] Implementation of the wave-propagation
process in detail.
The
traveling-wave process consists of a passive, sub-threshold propagation process
and a spiking mechanism, which ensures active (continuous) wave propagation. This
can be emulated by a (single) layer of interconnected integrate-and-fire
neurons, whose spike mechanism includes a refractory period to ensure forward
propagation (Koch
1999; Rasche 2007):
Example for a point:
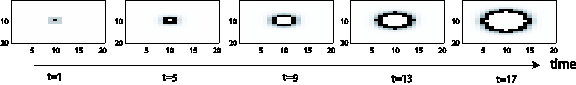
Example for two images:
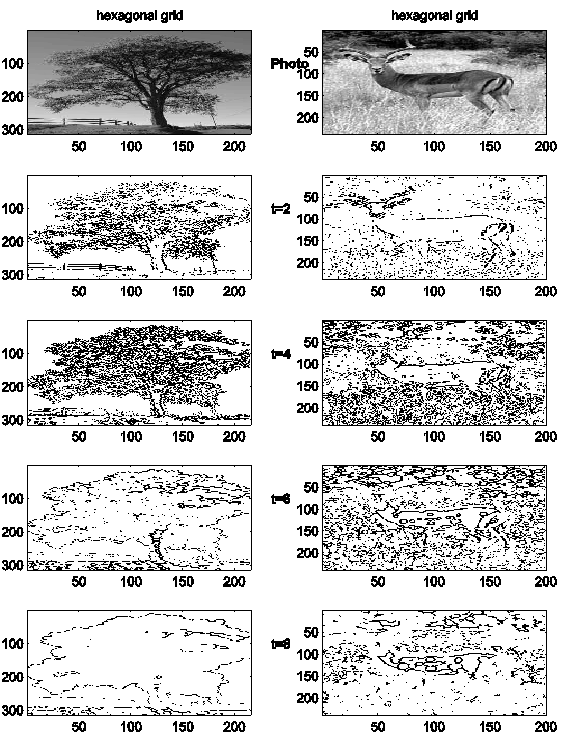
If the temporal evolvement is held
in an image you end up with a ‘landscape’.
Here an example for simple shapes:
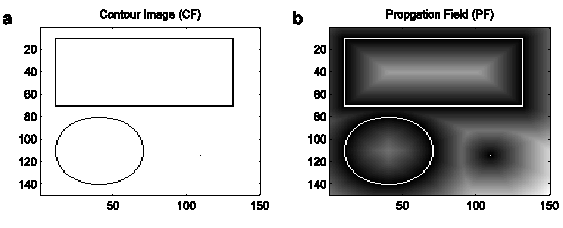
On the right you see that
the veins correspond to the symmetric axes!